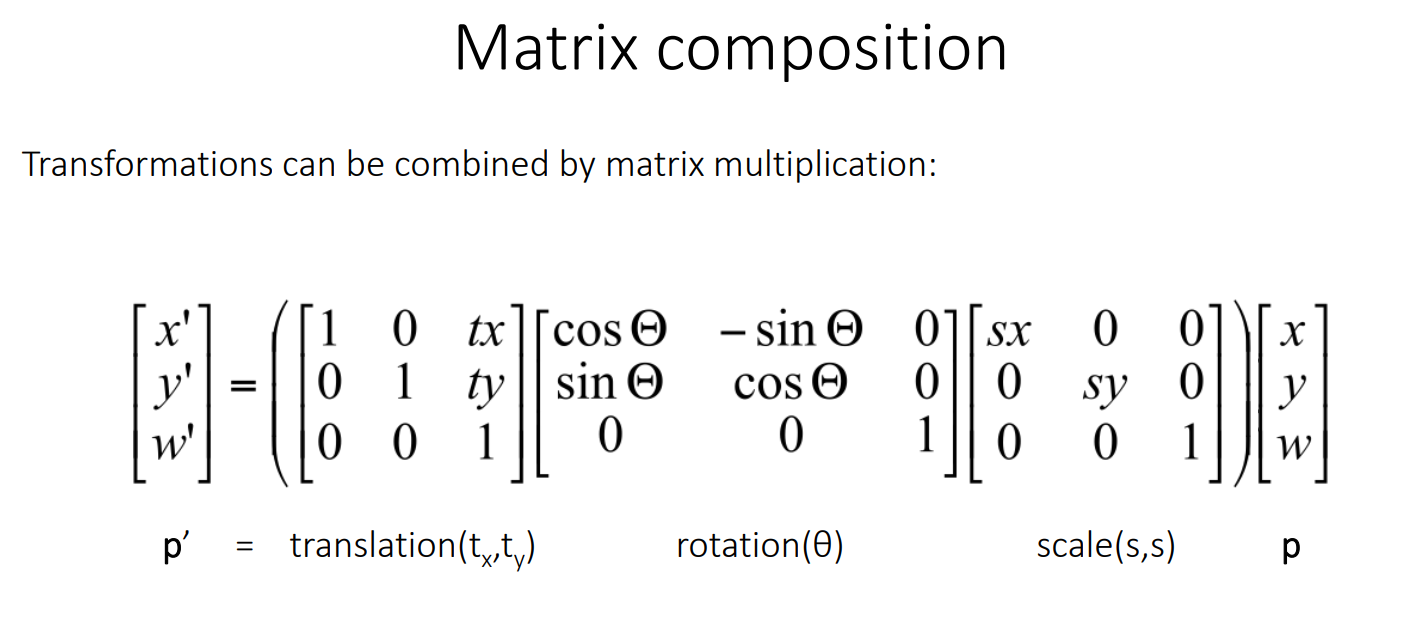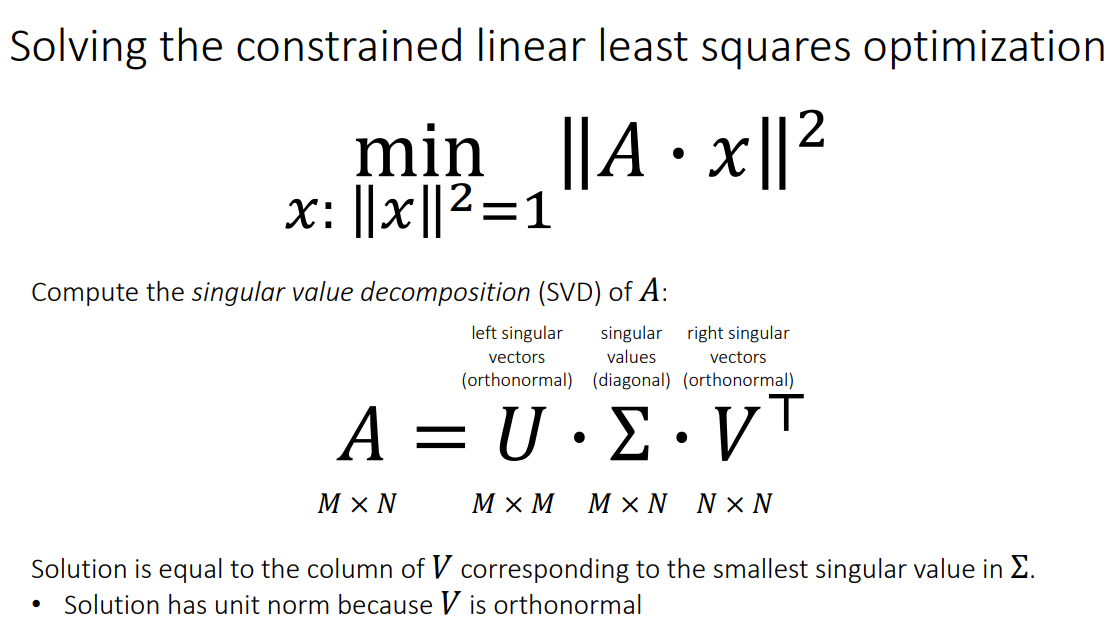instructor :
Loannis Gkioulekas . Yannis
# lecture 1
# Linear shift-invariant image filtering
线性性(Linearity): 线性系统满足叠加原理,即对于输入信号 f1 和 f2 以及常数 a 和 b,有:
L(af1+bf2)=aL(f1)+bL(f2)
其中,L 表示线性系统。
平移不变性(Shift-Invariance): 平移不变性表示系统的特性不随输入信号的位置改变而改变。即如果输入信号 f(x,y) 平移了 (x0,y0),则输出信号也相应平移相同的量:
L(f(x−x0,y−y0))=L(f)(x−x0,y−y0)
在图像处理中,线性平移不变滤波通常用卷积操作来表示:
# 均值滤波器(Mean Filtering)
主要用于平滑图像,减少噪声。其基本思想是用一个卷积核(通常是一个大小为 n×nn \times nn×n 的矩阵)在图像上移动,每个像素点的值用其邻域内所有像素的平均值代替。
##### 操作步骤:
- 确定卷积核的大小(如 3x3, 5x5)。
- 对图像中的每个像素点,计算其邻域内所有像素的平均值。
- 用计算得到的平均值代替当前像素点的值。
(I∗h)(x,y)=N1i=−2N∑2Nj=−2N∑2NI(x−i,y−j)
# 高斯滤波器(Gaussian Filtering)
基于高斯函数的线性滤波器,主要用于图像平滑和模糊处理。其特点是能保留图像的边缘细节,较少产生伪影。
# 操作步骤:
- 确定高斯核的大小和标准差(σ)。
- 生成高斯核,根据高斯函数计算每个核值。
- 使用高斯核对图像进行卷积操作,计算邻域内像素的加权平均值。
(I∗h)(x,y)=N1i=−2N∑2Nj=−2N∑2NI(x−i,y−j)
非线性滤波器,主要用于去除图像中的椒盐噪声。它通过取邻域内所有像素值的中值来替代当前像素点的值。
(I∗h)(x,y)=median{I(x+i,y+j)∣−2N≤i,j≤2N}
# 操作步骤:
- 确定滤波窗口的大小(如 3x3, 5x5)。
- 对图像中的每个像素点,取其邻域内所有像素值。
- 计算这些值的中值,用该中值替代当前像素点的值。
# Sobel 滤波器(Sobel Filter)
边缘检测滤波器,主要用于检测图像中的边缘。它通过计算梯度的大小和方向来识别图像中的显著变化。
# 操作步骤:
- 使用两个 3x3 的 Sobel 核,分别检测水平和垂直方向上的梯度。
- 对图像进行卷积操作,分别计算水平和垂直方向上的梯度图像。
- 计算梯度的大小和方向,得到边缘图像。
水平梯度:
Gx=⎣⎢⎡−1−2−1000121⎦⎥⎤∗I
垂直梯度:
Gy=⎣⎢⎡−101−202−101⎦⎥⎤∗I
综合梯度:
G=Gx2+Gy2
# 拉普拉斯滤波器(Laplacian Filter)
边缘检测滤波器,它通过计算图像的二阶导数来检测边缘。该滤波器对噪声敏感,通常在使用前需要对图像进行平滑处理.
# 操作步骤:
使用一个拉普拉斯核(如 3x3 的矩阵)。
对图像进行卷积操作,计算每个像素点的拉普拉斯值。
对拉普拉斯值进行阈值处理,得到二值化的边缘图像。
h(i,j)=⎣⎢⎡0101−41010⎦⎥⎤∗I
# 方框滤波器 (Box Filter)
是一种特殊的均值滤波器,其中每个卷积核元素的值相等,且其和为 1。与均值滤波器类似
Box Filter 与均值滤波器的公式相同:
(I∗h)(x,y)=N1i=−2N∑2Nj=−2N∑2NI(x−i,y−j)
####box filter
![image-20240727200023274]()
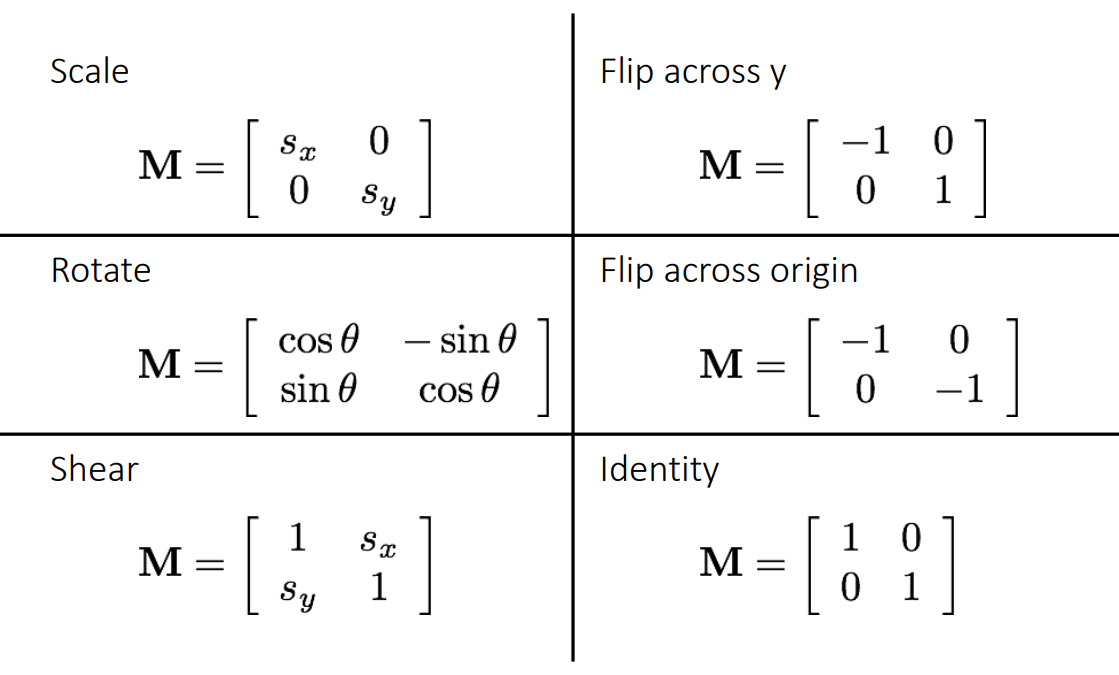
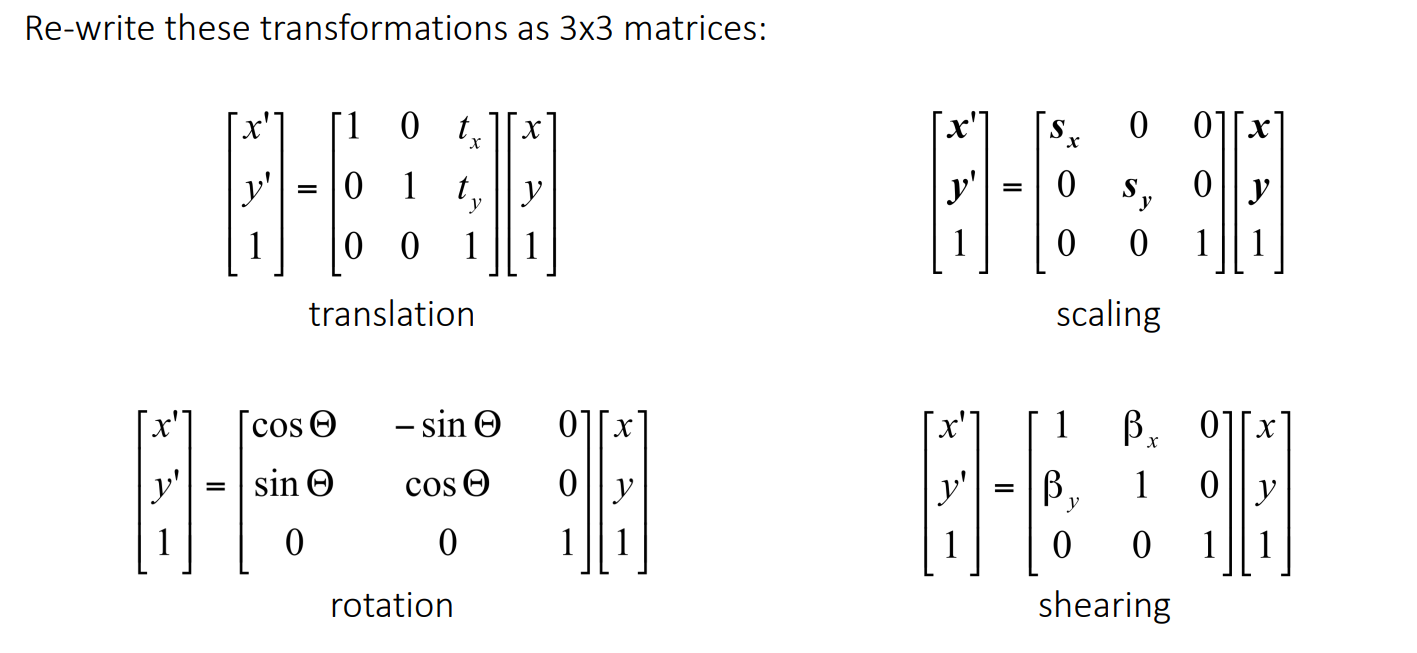
# Homogeneous coordinates
![]()
![image-20240727200206731]()
Multiplication order matters! Transformations are applied from right to left.
![image-20240727200254398]()
# Translation 2
\ \begin{pmatrix} x' \\ y' \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & t_x \\ 0 & 1 & t_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} x \\ y \\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \
# Euclidean 3
(x′y′)=⎝⎛cosθsinθ0−sinθcosθ0txty1⎠⎞⎝⎛xy1⎠⎞
# Similarity 4
(x′y′)=⎝⎛scosθssinθ0−ssinθscosθ0txty1⎠⎞⎝⎛xy1⎠⎞
# Affine 6
(x′y′)=⎝⎛ac0bd0txty1⎠⎞⎝⎛xy1⎠⎞
# Projective 8
⎝⎛x′y′w⎠⎞=⎝⎛adgbehcf1⎠⎞⎝⎛xy1⎠⎞
# Solving linear systems
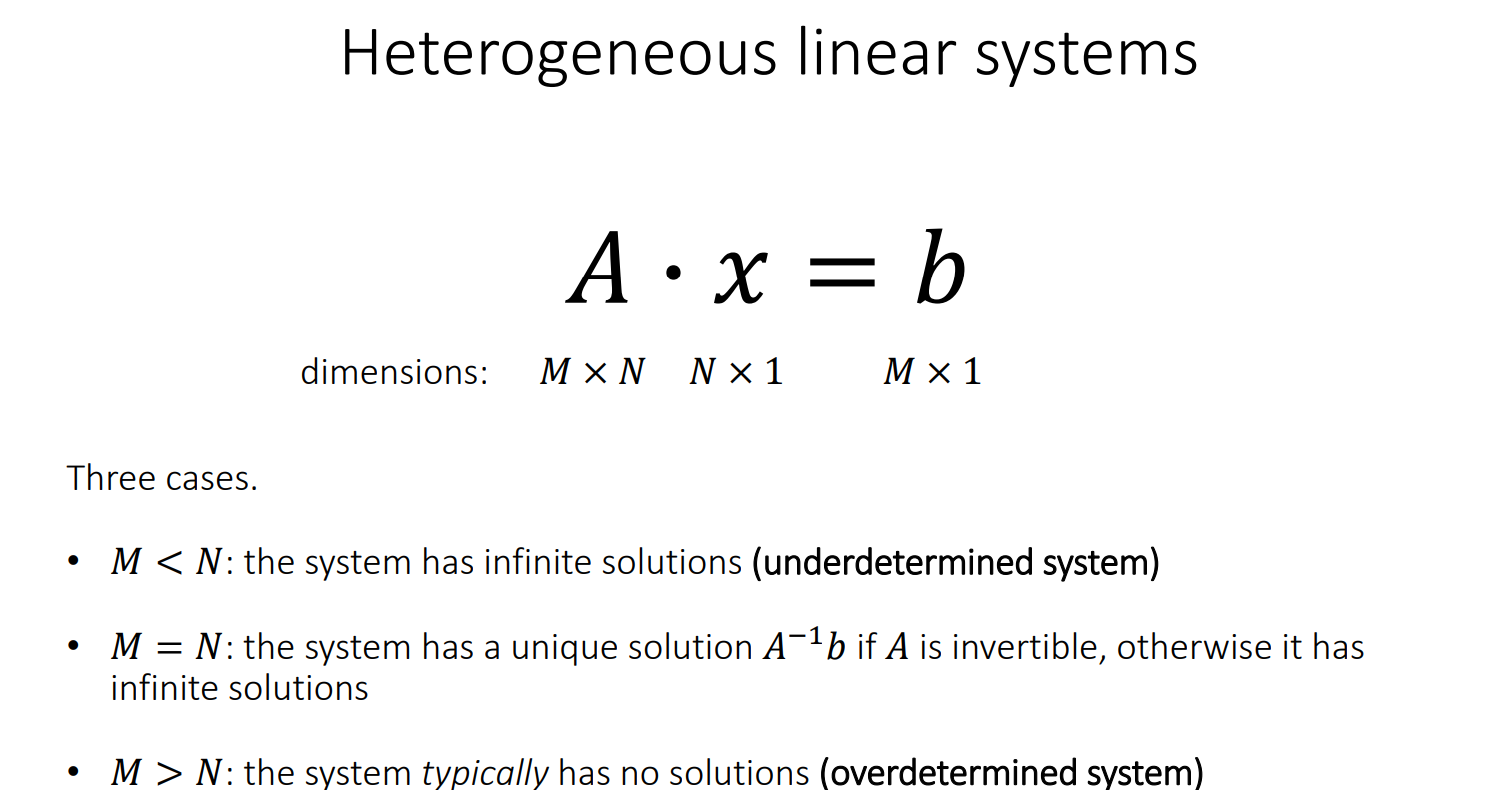
# Heterogeneous linear systems
![image-20240727201246348]()
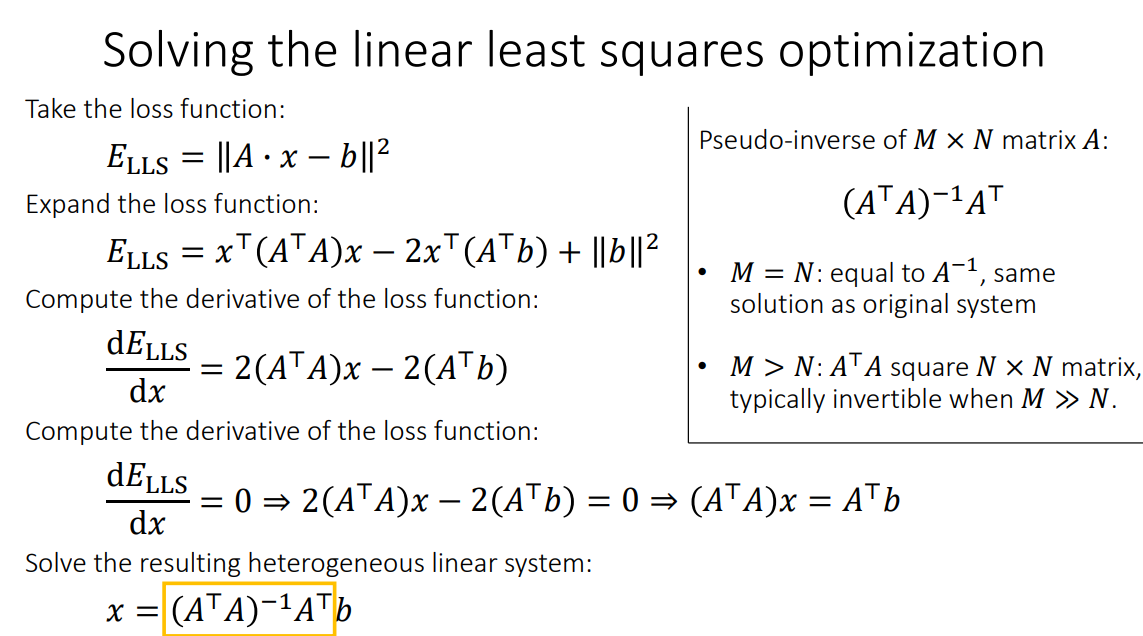
with the optimization problem:
xmin∥Ax−b∥2
![image-20240727201328214]()
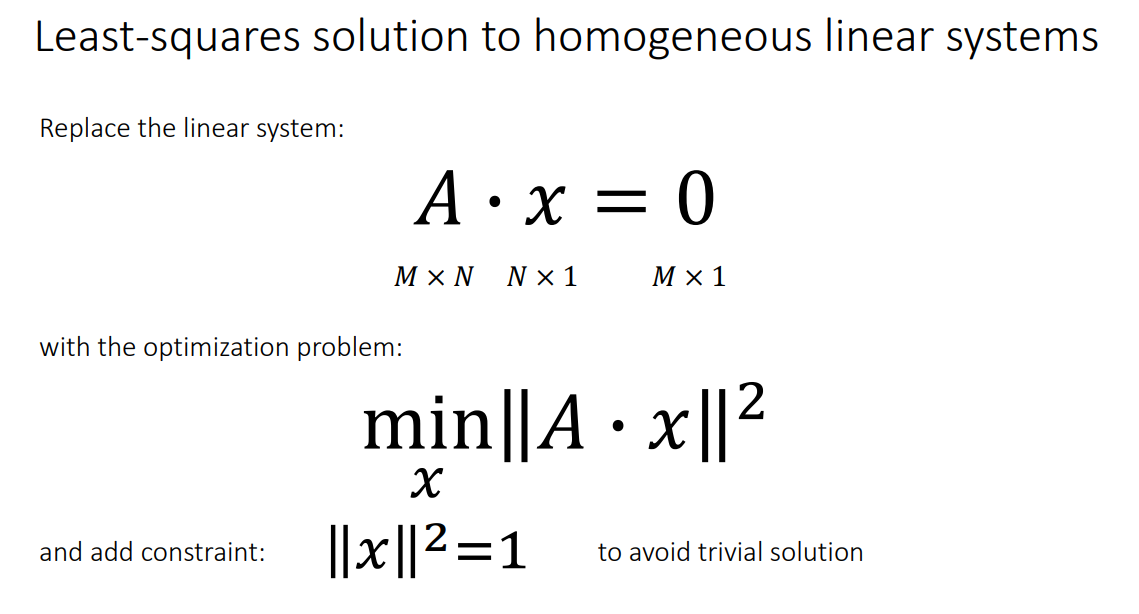
# Homogeneous linear systems
![image-20240727201451582]()
![image-20240727201517001]()
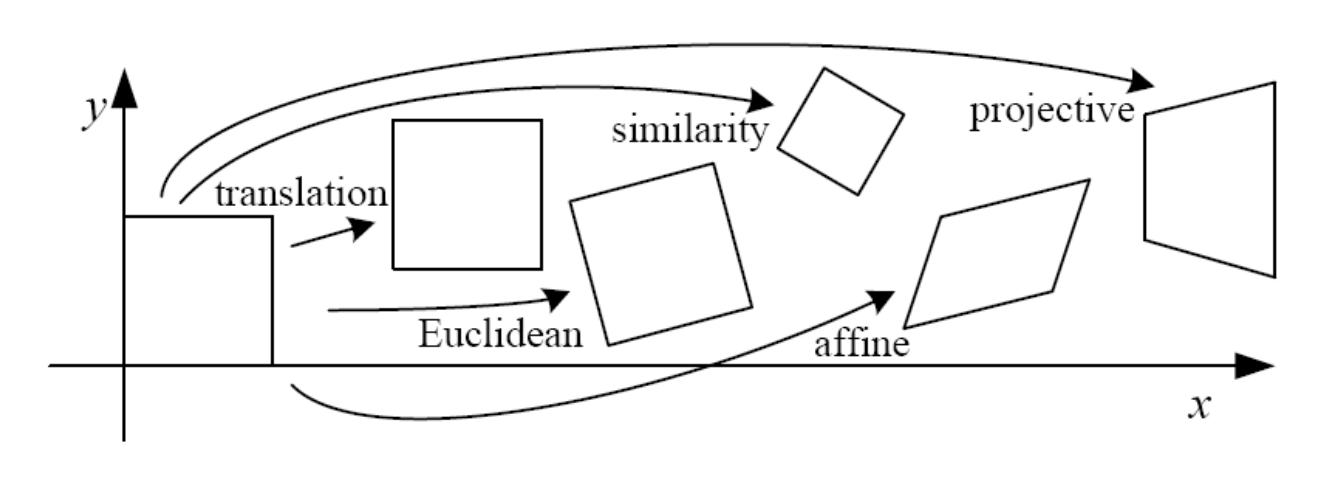
# 解决问题
- image A and B, find a way of transform to aligns image B to image A.
- Support we have already find 4 pairs of corresponding points by some method:
A:$ (x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), (x_3, y_3), (x_4, y_4)$
B:(x1′,y1′),(x2′,y2′),(x3′,y3′),(x4′,y4′)
We wish to find an affine transformation matrix T :
⎝⎛x′y′1⎠⎞=⎝⎛ad0be0cf1⎠⎞⎝⎛xy1⎠⎞
We can expand the matrix equation into two linear equations:
{x′=ax+by+cy′=dx+ey+f
For each pair of corresponding points, we have a set of such equations. For four pairs of corresponding points, we have eight equations:
⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧x1′=ax1+by1+cy1′=dx1+ey1+fx2′=ax2+by2+cy2′=dx2+ey2+fx3′=ax3+by3+cy3′=dx3+ey3+fx4′=ax4+by4+cy4′=dx4+dy4+f
We can write these equations in matrix form Ax=b, where:
A=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛x10x20x30x40y10y20y30y40101010100x10x20x30x40y10y20y30y401010101⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
x=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛abcdef⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
b=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛x1′y1′x2′y2′x3′y3′x4′y4′⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞
通过求解正常方程 $ATAx=ATb $,我们可以得到最小二乘解 X.
# Eigenvector
Av=λv
对于一个矩阵 A,如果存在一个非零向量 v 和一个标量 λ 使得Av=λv,那么 v 就是 A 的特征向量,λ 是对应的特征值。
# SVD
A=UΣVT
U: Left Singular Vectors for AAT U=[u1,u2,…,uM]
Σ: Singular Values
Σ=⎝⎜⎜⎜⎜⎛σ10⋮00σ2⋮0⋯⋯⋱⋯00⋮σr⎠⎟⎟⎟⎟⎞whereσi=λi
V: Right Singular Vectors for ATA V=[v1,v2,…,vN]
为了最小化 ∥Ax∥2 并满足 ∥x∥2=1,我们可以利用 SVD 的结果:
将优化问题转换为标准形式: 通过 SVD,我们可以将原优化问题转化为:
∥Ax∥2=∥UΣVTx∥2
因为 U 是正交矩阵,保持向量的范数不变,所以我们可以忽略 U:
minx∥ΣVTx∥2
定义新变量: 令 $ y=V^Tx$,则 y 也是一个单位向量(因为 V 是正交矩阵)。我们需要最小化:
∥Σy∥2
选择最小奇异值对应的方向: Σ 是一个对角矩阵,其中的奇异值按降序排列。为了使 ∥Σy∥2 最小,y 应该选择与最小奇异值对应的方向。
恢复原变量: 最后,利用 y=VTx,我们可以求出满足 ∥x∥2=1 的 x
###Basic reading
- Szeliski textbook, Sections 2.1, 3.6.
- Hartley and Zisserman textbook, Section 2.
# lecture 2